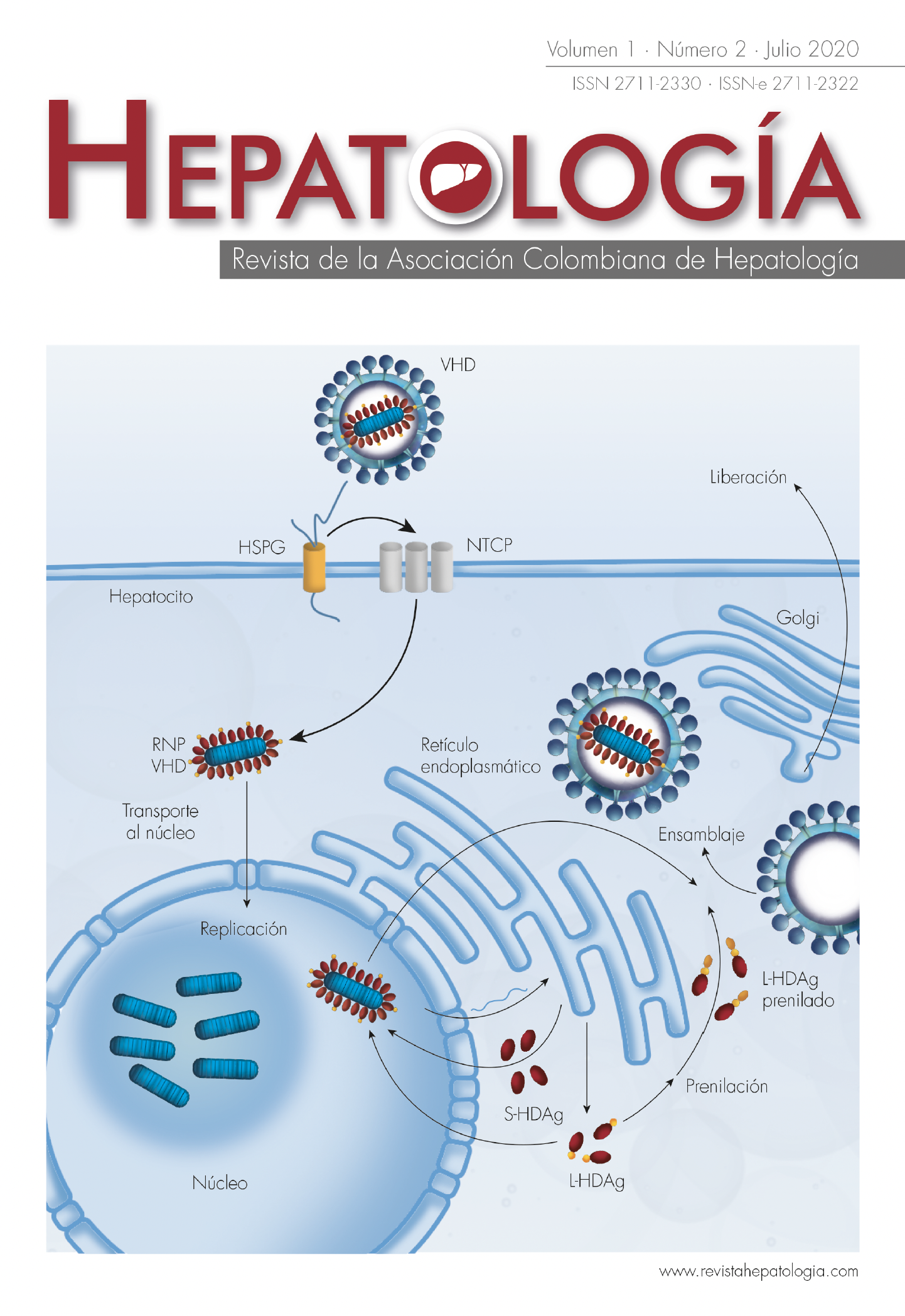
DILI: a challenge
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.52784/27112330.118Abstract
Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) is a rare condition with a varied clinic. Currently, almost 1,000 drugs and herbal products have been described that can cause liver damage, with complications so severe that they can compromise the lives of patients, who may eventually require a liver transplant as the only alternative for survival. DILI continues to be the main reason for suspending the advancement of new drugs in their development phases.
Downloads
References
Andrade RJ, Chalasani N, Björnsson ES, Suzuki A, Kullak-Ublick GA, Watkins PB, et al. Drug-induced liver injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2019;5:58. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-019-0105-0.
Machancoses-Primo A, Pitarch-Flors R. Calculadoras. DILI Drug-induced liver injury. Escala Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences/Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (CIOMS/RUCAM). Valencia, España: Rapid Critical Care Consult; 2013. Acceso 26 de junio de 2020. Disponible en https://www.rccc.eu/scores/RUCAM.html.
Proctor WR, Foster AJ, Vogt J, Summers C, Middleton B, Pilling MA, et al. Utility of spherical human liver microtissues for prediction of clinical drug-induced liver injury. Arch Toxicol 2017;91:2849-2863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-017-2002-1.
Bell CC, Hendriks DFG, Moro SML, Ellis E, Walsh J, Renblom A, et al. Characterization of primary human hepatocyte spheroids as a model system for drug-induced liver injury, liver function and disease. Sci Rep 2016;6:25187. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep25187.
Church RJ, Kullak-Ublick GA, Aubrecht J, Bonkovsky HL, Chalasani N, Fontana RJ, et al. Candidate biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of drug-induced liver injury: An international collaborative effort. Hepatology 2019;69:760-773. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29802.
Bessone F, Hernández N, Mendizábal M, Sánchez A, Paraná R, Arrese M, et al. Cuando la creación de un consorcio proporciona respuestas útiles: experiencia de la Latin American DILI Network (LATINDILIN). Clin Liver Dis 2019;13:S17-S23. https://doi.org/10.1002/cld.840.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Hepatología’s authorship policy is based on the criteria established by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) to credit a person for their work while assigning them responsibility for its publication.
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |