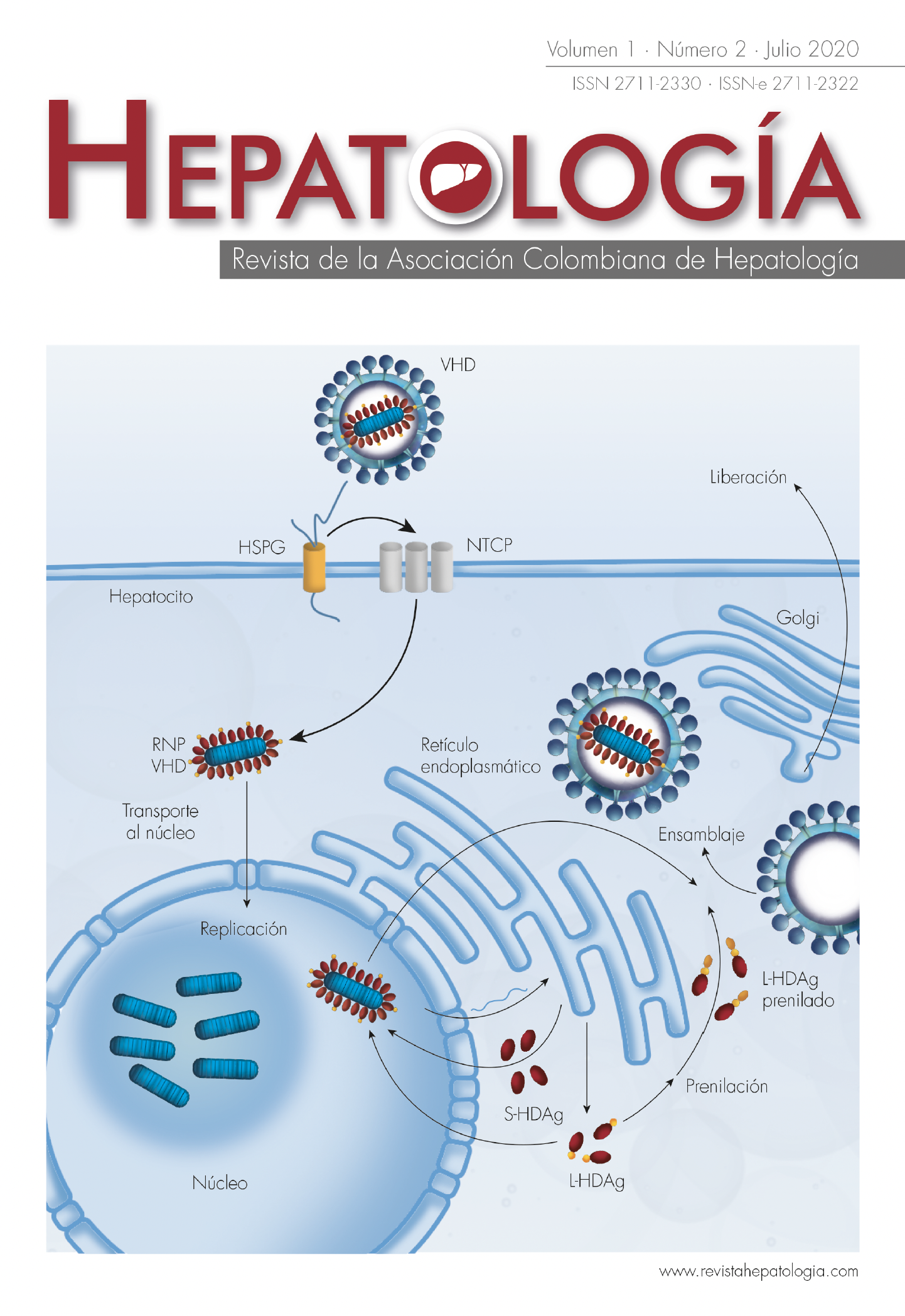
Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome: a case report and literature review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.52784/27112330.125Keywords:
Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome, hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, epistaxis, arte- riovenous malformations.Abstract
Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome, also known as hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, is an autosomal dominant low-prevalence disease, characterized by thin blood vessel walls, leading to arteriovenous malformations, mainly in the brain, lung and liver, but can potentially affect any other organ. The main clinical manifestation is recurrent epistaxis; however, other manifestations may also appear, such as hemoptysis or gastrointestinal bleeding, and mucocutaneous telangiectasias, among others. Its clinical expression varies from patient to patient and the diagnosis is usually based on Curacao criteria. We present the case of a patient with a 12-year history of recurrent epistaxis, who was diagnosed with Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome two years ago. She was referred to the Hepatology service due to liver findings, in addition to brain and pulmonary arteriovenous malformations. The optimal management of hemorrhagic telangiectasia in this patient by the different specialists, supported by imaging studies, has allowed the patient to have a good quality of life. The case of this 46-year-old patient is presented, and a brief literature review is also provided.
Downloads
References
Shovlin CL. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome). Massachusetts, Estados Unidos: Wolters Kluwer Health; 2019. Uptodate. Acceso 13 de noviembre de 2019. Disponible en https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-manifestations-and-diagnosis-of-hereditary-hemorrhagic-telangiectasia-osler-weber-rendu-syndrome.
Robaina-Cabrera DM, Verde-González MP, Tarazona-Chocano B, Amado-Fernández C, Zarrabeitia-Puente R. Telangiectasia hemorrágica hereditaria: enfermedad de Rendu-Osler-Weber. FMC 2016;23:446-458. https://doi.org/https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=5958298.
Robert F, Desroches-Castan A, Sabine B, Dupuis-Girod S, Feige JJ. Future treatments for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2020;15:p.10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-019-1281-4.
Kritharis A, Al-Samkari H, Kuter DJ. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: diagnosis and management from the hematologist's perspective. Haematologica 2018;103:1433-1443. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2018.193003.
Mosquera-Klinger GA, Gálvez-Cardenas K, Valencia-Ruíz AM. Diagnóstico y tratamiento de pacientes con telangiectasia hemorrágica hereditaria (Síndrome de Rendu-Osler-Weber) en un hospital universitario en Colombia. Rev Colomb Gastroenterol 2019;34:152-158. https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.280.
Sandoval-Martínez DK, García-Ayala E, Ramírez-Figueroa S, Torres-Rodríguez KJ, Velandia-Avendaño MC, Villamizar-Castro JF, et al. SÍndrome de Rendu Osler Weber en una adolescente en Colombia. Reporte de un caso de autopsia. Biosalud 2018;17:83-89. https://doi.org/http://dx.doi.org/10.17151/biosa.2018.17.1.8
Kühnel T, Wirsching K, Wohlgemuth W, Chavan A, Evert K, Vielsmeier V. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 2018;51:237-254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2017.09.017.
Karlsson T, Cherif H. Mutations in the ENG, ACVRL1, and SMAD4 genes and clinical manifestations of hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia: Experience from the Center for Osler's Disease, Uppsala University Hospital. Ups J Med Sci 2018;123:153-157. https://doi.org/10.1080/03009734.2018.1483452.
Blivet S, Cobarzan D, Beauchet A, El Hajjam M, Lacombe P, Chinet T. Impact of pulmonary arteriovenous malformations on respiratory-related quality of life in patients with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. PloS one 2014;9:e90937. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0090937.
Garg N, Khunger M, Gupta A, Kumar N. Optimal management of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. J Blood Med 2014;5:191-206. https://doi.org/10.2147/JBM.S45295.
McDonald J, Bayrak-Toydemir P. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Editorials and perspectives. Haematologica 2005;90:728-732.
Macri A, Wilson AM, Shafaat O, Sharma S. Osler-Weber-Rendu disease (Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia, HHT). Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020. Acceso 13 de enero de 2020. Disponible en https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482361/.
Jackson SB, Villano NP, Benhammou JN, Lewis M, Pisegna JR, Padua D. Gastrointestinal manifestations of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT): A systematic review of the literature. Dig Dis Sci 2017;62:2623-2630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-017-4719-3.
Brinjikji W, Iyer VN, Yamaki V, Lanzino G, Cloft HJ, Thielen KR, et al. Neurovascular manifestations of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: A consecutive series of 376 patients during 15 years. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2016;37:1479-1486. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A4762.
Faughnan ME, Palda VA, Garcia-Tsao G, Geisthoff UW, McDonald J, Proctor DD, et al. International guidelines for the diagnosis and management of hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. J Med Genet 2011;48:73-87. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmg.2009.069013.
Tabakow P, Jarmundowicz W, Czapiga B, Czapiga E. Brain abscess as the first clinical manifestation of multiple pulmonary arteriovenous malformations in a patient with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber disease). Folia Neuropathol 2005;43:41-44.
Nollen GJ, Kodde J, Beek AM, Res JC, van Rossum AC. Quadricuspid pulmonary valve and left pulmonary artery aneurysm in an asymptomatic patient assessed by cardiovascular MRI. Neth Heart J 2013;21:196-198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12471-011-0115-3.
Baldi S, Rostagno RD, Zander T, Rabellino M, Maynar M. Oclusión de una fístula arteriovenosa pulmonar con el tapón vascular Amplatzer. Arch Bronconeumol 2007;43:239-241. https://doi.org/10.1157/13100544.
Olivencia L, Soto JM, Martín de la Fuente P. Embolismo paradójico a través de foramen oval permeable coincidente con embolismo pulmonar. Med Intensiva 2012;36:450-451.
Gossage JR. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: Epidemiology, etiology, and pathology in adults. Massachusetts, Estados Unidos: Wolters Kluwer Health; 2019. Uptodate. Acceso 26 de noviembre de 2019. Disponible en https://www.uptodate.com/contents/pulmonary-arteriovenous-malformations-epidemiology-etiology-and-pathology-in-adults.
Cottin V, Dupuis-Girod S, Lesca G, Cordier JF. Pulmonary vascular manifestations of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler disease). Respiration 2007;74:361-378. https://doi.org/10.1159/000103205.
Riera-Mestre A, Ribas J, Castellote J. Tratamiento de la telangiectasia hemorrágica hereditaria en el paciente adulto. Med Clin 2019;152:274-280. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medcli.2018.09.015.
Tortora A, Riccioni ME, Gaetani E, Ojetti V, Holleran G, Gasbarrini A. Rendu-Osler-Weber disease: a gastroenterologist's perspective. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2019;14:130. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-019-1107-4.
Buscarini E, Danesino C, Olivieri C, Lupinacci G, Zambelli A. Liver involvement in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia or Rendu-Osler-Weber disease. Dig Liver Dis 2005;37:635-645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2005.04.010.
Leitão P, Carvalho A, Guerra C, Gonçalves J, Ramos I. Congestive cirrhosis in Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome: A rare case report. Radiol Case Rep 2017;13:51-54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radcr.2017.10.011.
Gaillard S, Dupuis-Girod S, Boutitie F, Rivière S, Morinière S, Hatron PY, et al. Tranexamic acid for epistaxis in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia patients: a European cross-over controlled trial in a rare disease. J Thromb Haemost 2014;12:1494-1502. https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.12654.
Chin CJ, Rotenberg BW, Witterick IJ. Epistaxis in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: an evidence based review of surgical management. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2016;45:3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40463-016-0116-8.
Molinos-Castro S, Pesqueira-Fontán PM, Díaz-Peromingo JA. Telangiectasia hemorrágica hereditaria: tratamiento farmacológico. Rev Med Chil 2009;137:695-700.
Hsu YP, Hsu CW, Bai CH, Cheng SW, Chen C. Medical treatment for epistaxis in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: A meta-analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2019;160:22-35. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599818797316.
Harrison L, Kundra A, Jervis P. The use of thalidomide therapy for refractory epistaxis in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia: systematic review. J Laryngol Otol 2018;132:866-871. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022215118001536.
Parambil JG, Woodard TD, Koc ON. Pazopanib effective for bevacizumab-unresponsive epistaxis in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Laryngoscope 2018;128:2234-2236. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.27129.
ClinicalTrials.gov. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Pazopanib for the treatment of epistaxis in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Bethesda, Maryland: U.S. National Library of Medicine; 2019. Acceso 11 de enero de 2020. Disponible en https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03850730.
Richer SL, Geisthoff UW, Livada N, Ward PD, Johnson L, Mainka A, et al. The Young's procedure for severe epistaxis from hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Am J Rhinol Allergy 2012;26:401-404. https://doi.org/10.2500/ajra.2012.26.3809.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Hepatología’s authorship policy is based on the criteria established by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) to credit a person for their work while assigning them responsibility for its publication.
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |